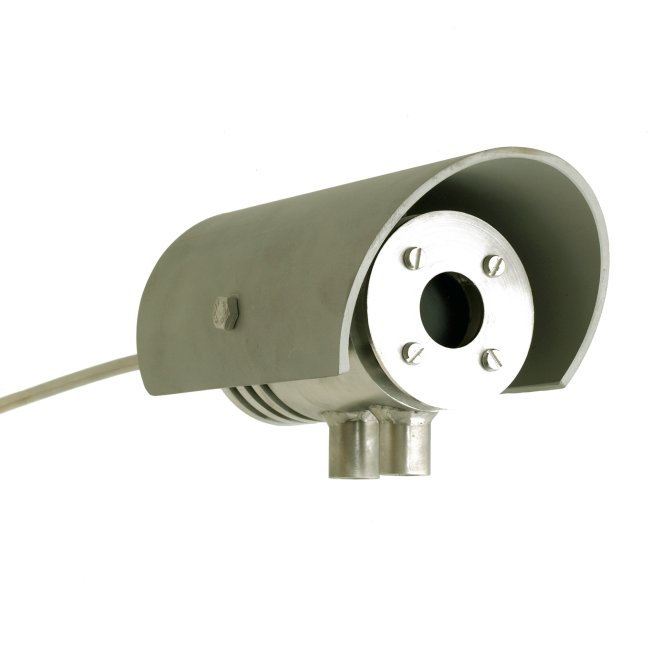
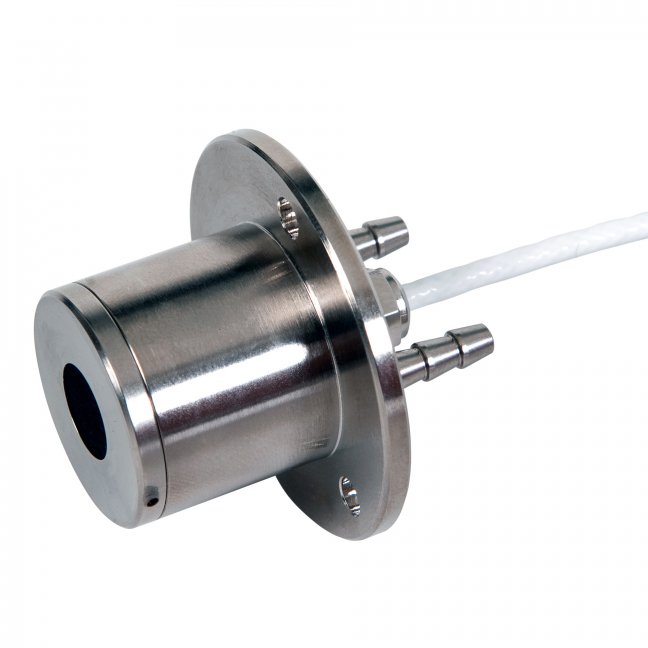
HF02 is used in alarm systems, using the heat flux measurement to issue a warning in case of high thermal radiation exposure of equipment or personnel. It is typically installed close to a flare. A common assumption is that the heat flux level in a safe environment for personnel must not exceed 5 x 10³ W/m² (or 1.5 x 10³ BTU/(hr∙ft²)). Above that heat flux level, or when the temperature of the sensor body exceeds 70 °C, an alarm is activated. A typical alarm system will include multiple HF02 sensors, all aimed at the main source of radiation, as well as other decision-supporting devices such as camera systems and temperature sensors. The sensor in HF02 measures the heat flux to its black (absorbing) surface, in the plane of the sensor, from a source in the field of view angle. It offers a measurement of the effective exposure for personnel and equipment from a source in the direction it is aimed at the location of the sensor. As the detector is essentially open (it has no protective windows) the measurement is influenced by wind in the same way as any exposed surface such as clothing worn by personnel or the surface of equipment; increased wind speed leads to a reduction of the measured heat flux. Rain on the detector can also lead to cooling and a reduction of the measured heat flux.